Custom Canvas Prints & Wall Art - Prints4sure
Your Life, Your Canvas: The Making
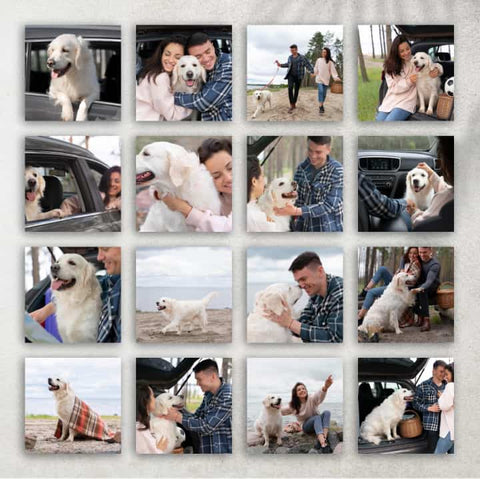
Reflect & Revisit: Dive deep into your memories. Whether it's the holiday you took last summer, a candid laughter shared with a loved one, or even that mesmerizing sunset from your balcony. Your memories are your treasures.
Creation with Precision: With just a few taps, upload your selected memories onto the Prints4Sure platform. Customize them, choose the perfect size and layout, and let your creativity flow. Every adjustment you make ensures your canvas tells the story just the way you remember it.
Swift & Seamless: Once your design is complete, simply place your order. With Prints4sure's commitment to quality and swift, free delivery, your custom canvas prints will be adorning your walls in no time.
Creating Your Personal Narrative Through Art
The Journey Map: From the alleyways of Venice to the peaks of the Himalayas, trace your adventures with a series of canvas prints. A visual map of your journeys, reminding you of the paths tread and paths yet to explore.
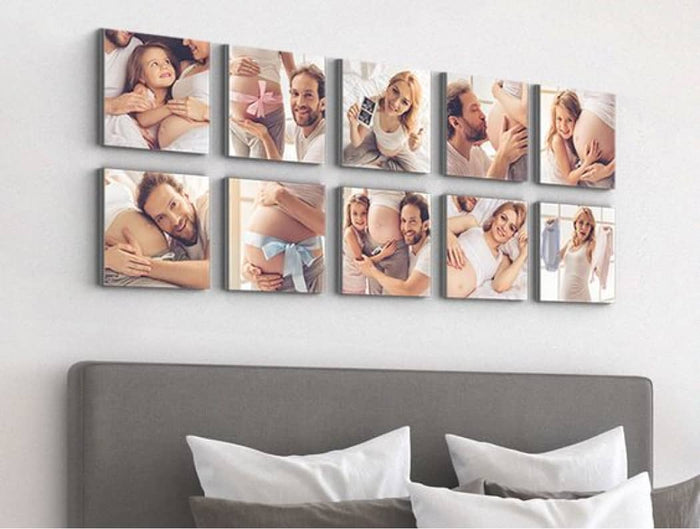
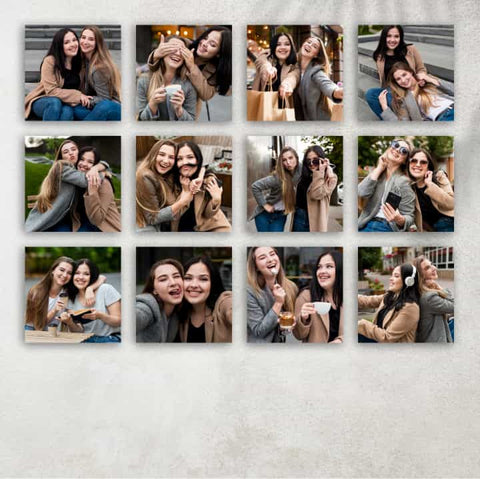
Moments that Matter: Maybe it's your child's first step, or the first dance at your wedding. These fleeting moments, when captured on canvas, become eternal, reminding you of life's little joys.
Artistic Ambitions: Have a sketch, painting, or digital art that you've crafted? Why not transform it into a custom canvas? Showcase your talent and make your living space truly unique.
The Prints4Sure Advantage
Clarity & Quality: Memories might fade, but with Prints4Sure, your canvas remains as vivid as the moment itself. High-definition prints ensure every emotion, every color, every detail stands out.
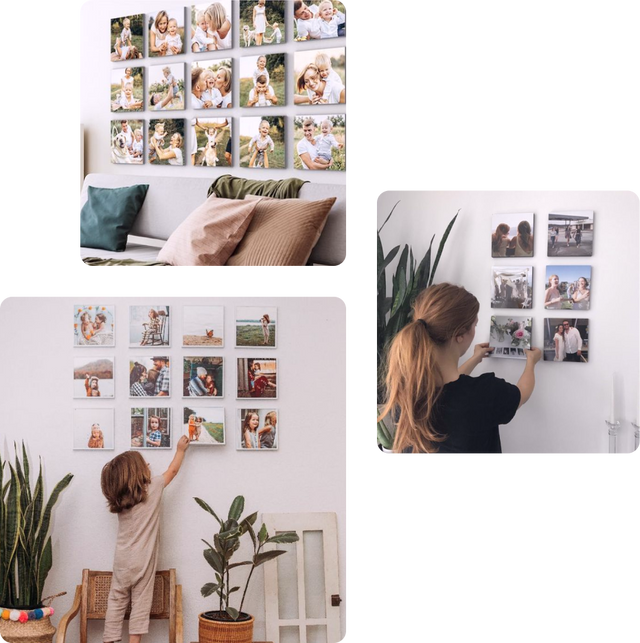
Hassle-free Hanging: No need for drills, nails, or hammers. With the innovative adhesive technique, hang your canvas with ease, and even relocate without leaving behind any residue.
A Helping Hand: Whether you need assistance with design, have queries about the process, or face any issues, the Prints4Sure team is always ready to guide and assist, ensuring your canvas creation journey is smooth.
Ideas to Inspire
- Chronicles of Growth: Capture your child's journey from infancy to their graduation day. A wall dedicated to their milestones, a testament to their journey of growth.
- Dream Destinations: Have a list of places you wish to visit? Create a vision board with pictures of these dream destinations, a daily reminder of adventures waiting to be embarked upon.
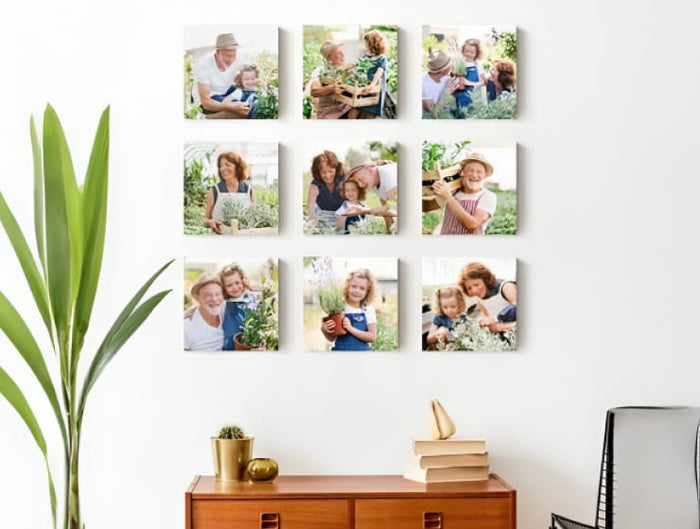
- Homage to Hobbies: From a beautiful crochet pattern you designed to photographs of your garden blooms – let your hobbies find a place on your wall.
A Canvas Commitment
With Prints4Sure, it's not just about printing photos; it's about capturing emotions, cherishing memories, and presenting them in the most beautiful, lasting manner. From selecting the right materials to ensuring the colors are perfect, every step is taken with meticulous care.
To Conclude
Life is a beautiful, winding journey, with each day adding a new chapter, a new memory. Custom canvas prints allow you to capture these moments, immortalizing them for years to come. With Prints4sure, this transformation is just a few clicks away. Dive into your memories, bring them alive on canvas, and let your walls narrate your unique story. After all, there's no storyteller like a home filled with cherished memories.













 (4.9/5)
(4.9/5)
















